It is becoming increasingly clear that can benefit our mental health and wellbeing. But a new study by my colleagues and me shows that you don’t have to actually be in nature to reap the rewards. Simply directing your gaze towards natural elements, even in the middle of a city, can enhance wellbeing.
Our paper, , used eye-tracking technology to explore how focusing on natural versus man-made elements affects mental health.
Urban living, with its fast pace and high levels of stress, numerous mental health issues, including anxiety and depression.
Our research team, which was led by me and consisting of my colleagues Brian Rizowy and Assaf Shwartz, recruited 117 adults for the study. Participants were randomly assigned to one of three groups: one that focused on natural elements such as trees (green group), one that focused on man-made elements such as buildings (grey group) and a third group that focused on a mix of both (mixed group).
Each participant wore specialised eye-tracking glasses during a 45-minute guided walk around town and the campus. The route included ten designated stopping points designed to emphasise either natural or man-made elements, depending on the group.
Before and after the walk, participants completed surveys assessing their mood, anxiety levels and the restorative quality of the walk. The surveys included standardised measures such as the and the .
The eye-tracking glasses recorded where participants were looking throughout the walk, allowing researchers to quantify the amount of time spent focusing on green (natural) or grey (man-made) elements. In fact, our technique offered a precise and objective measure of visual engagement, strengthening the link between nature exposure and improved wellbeing. The data confirmed that each group really did spend more time looking at the scenery we had asked them to focus on.
The results were striking. Participants who focused more on green elements reported significant improvements in mood and reductions in anxiety compared to those who focused on grey elements. And they showed higher levels of positive emotions and lower levels of anxiety after the walk. They also reported feeling more refreshed and rejuvenated.
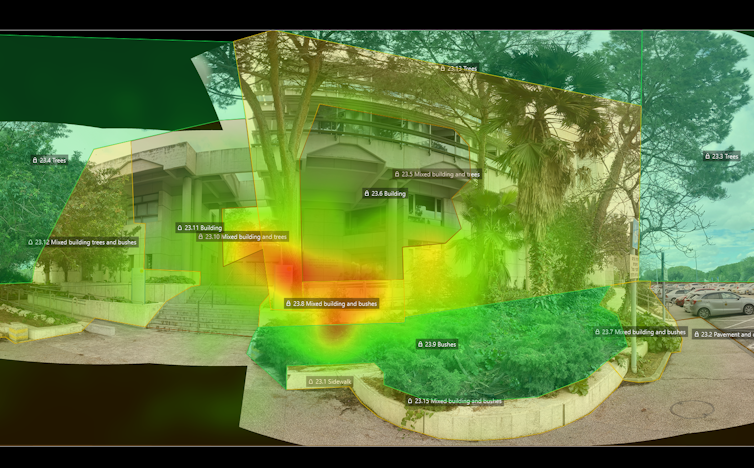
In contrast, the grey group did not show these improvements, and the mixed group had intermediate results, suggesting that even a partial focus on nature can be beneficial.
Implications for urban planning
These findings have important implications for urban planning and mental health practices. Designing urban spaces that incorporate natural elements and encourage visual engagement with nature could help reduce the mental health burden of city living.
For instance, planners could prioritise green spaces, tree-lined streets, parks and ponds that invite people to pause and take in the natural beauty.
The findings could also be useful for mental health professionals. For example, they may want to incorporate guided attention exercises into therapy, encouraging patients to specifically focus on natural elements during walks or other outdoor activities. This simple, cost-effective strategy could enhance traditional treatments for anxiety and depression.
The study highlights the importance of visual engagement with nature, providing robust evidence that the mental health benefits of nature are closely tied to where we focus our attention.
For the average person, this study suggests an easy way to boost mental health: spend more time looking at trees, flowers and other natural elements. Whether during a daily commute, a walk in the park or a weekend hike, consciously directing your gaze towards nature could make a significant difference in how you feel.
Our research underscores the potential for simple, everyday actions to have a profound impact on mental health. As urban areas continue to grow, integrating natural elements into cityscapes and encouraging people to engage visually with these elements could play a crucial role in enhancing public wellbeing.
Cyhoeddir yr erthygl Saesneg hon gan Dr Whitney Fleming o’r Ysgol Gwyddorau Amgylcheddol a Naturiol yn wreiddiol o dan drwydded creative commons gan The Conversation. Mae 'The Conversation' yn safle sy’n galluogi academyddion i ysgrifennu’n uniongyrchol er mwyn rhannu eu harbenigedd gyda’r cyhoedd. Darllenwch yr erthygl wreiddiol




